

|
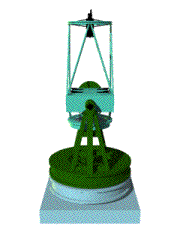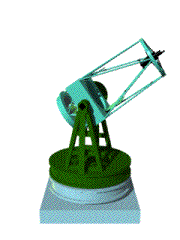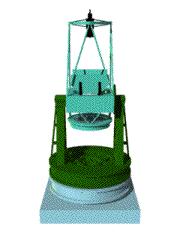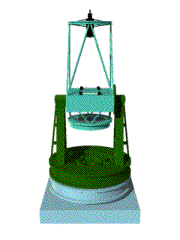
An astronomical telescope is an instrument designed
to collect faint light from celestial objects.
Light travelling from far in the distance of the universe
is collected into the focus of the telescope and
makes an image of a celestial body at the focus.
We see this image via eyepiece or
record the image by the detector,
and we can know some of the universe.
 |
|
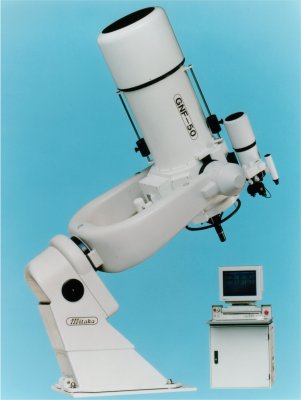
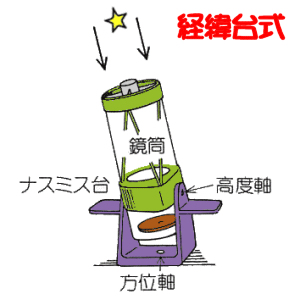
In general a typical telescope consists of a body, where a primary mirror collecting light is set, and a mount, which supports the body. A telescope is classified into two major types, refractor and reflector, whether it uses a lens or a reflecting mirror as a primary mirror. Furthermore, there are several types of the focus. A mount is also classified into two major types, an equatorial type and an alto-azimuth type. |
|
 |
 |
|---|---|
|
Provided by Mitaka Kohki Co., Ltd. |
|
|
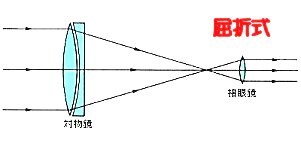
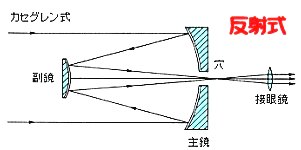
An astronomical telescope is classified into a refractor, where light is collected by a convex lens, and a reflector, where light is collected by a concave mirror. Since it is difficult to make and hold a large lens, the aperture limit of the refractor is about 1 meter. Hence, all of the big telescope are the reflector. |
|
|
 |
|
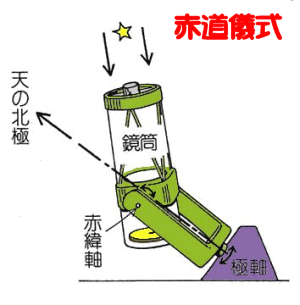
Due to the spin of the Earth,
celestial objects revolve every day
in 15 degree per hour (diurnal motion).
In order to observe a celestial body from the ground,
a telescope must track and guide the body.
|
|
 |
 |
 Go to Submenu
Go to Submenu Go to Menu
Go to Menu
自然科学書出版 裳華房 SHOKABO Co., Ltd.