

|
If a stellar spectrum is seen,
the line spectrum has overlapped on the continuum spectrum.
A stellar spectrum can be classified into some models from the appearance pattern of the line spectrum mainly.
Now, the Harvard System (O, B, A, F, G, K, M type) which classifies a spectrum in order of surface temperature is foundations, moreover, MK classification which attached the luminosity class (I-V) is used, which expresses stellar true brightness (absolute magnitude). How to write, such as A0V and M2III, is the systems of MK classification. If a stellar spectral type can be known, the feature of stars, such as a surface temperature and a stellar size, can be known easily. Moreover, if a line spectrum is investigated in detail, stellar physical character, such as surface temperature, a stellar size, chemistry composition, a motion of the atmosphere, and rotation speed, can be known in more detail. In this section, we introduce two typical stellar spectral classification. 星のスペクトルを見ると,紫から赤までのびた連続スペクトルの上に種々の線スペクトルが重なっています. 主にその線スペクトルの出現パターンから星のスペクトルをいくつかの型に分類することができます. 現在では表面温度の順番にスペクトルを分類するハーバード式分類法(O,B,A,F,G,K,M型)を基本とし, それに星の真の明るさ(絶対等級)を表す光度階級(I〜V)を添えたMK分類が使われています. A0V,M2IIIといった書き方がMK分類の方式です. 星のスペクトル型がわかると, およその表面温度や星の大きさなど基本的な星の特徴を簡単に知ることができるので非常に便利です. 恒星の天文学でさかんにスペクトル型が使われているのはそのためです. なお,線スペクトルを精細に調べると表面温度や星の大きさ,化学組成,大気の動き,自転速度など, 星の物理的性質をさらにくわしく知ることができます.これをスペクトル線解析と呼んでいます. ここでは恒星の分類について,代表的な分類法2種類を紹介しましょう.
|
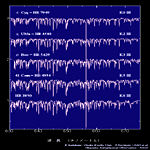
Sequence of Spectral Type
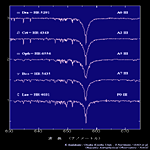
| Super Giant (Ia,Ib) <wavelength 380-700nm> | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 O7-A0 type |
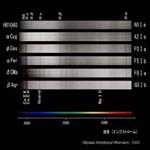 A0-G0 type |
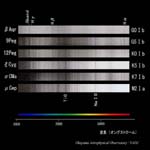 G0-M2 type |
||
| Super Giant (Ia,Ib) <Hα 656.3nm> | ||||
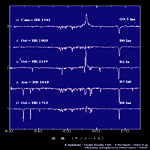 O9.5-B8 type |
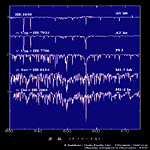 A0-M2 type |
|||
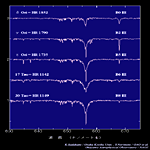
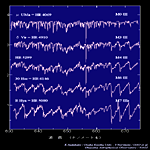
| Giant (III) <wavelength 380-700nm> | ||||
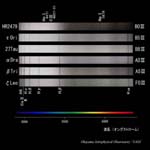 B0-F0 type |
 F0-K0 type |
 K0-M0 type |
 M0-M6 type |
|
| Giant (III) <Hα 656.3nm> | ||||
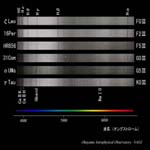
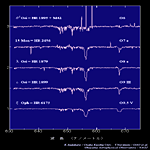 O6-O9.5 type |
 B0-B8 type |
 A0-F0 type |
 G0-G9 type |
|
 K0-K6 type |
 M0-M7 type |
|||
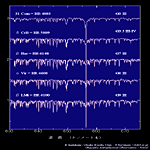
| Main Sequence Star (IV,V) <wavelength 380-700nm> | ||||
 O7-A0 type |
 A0-G0 type |
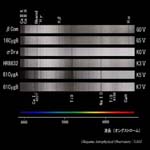 G0-K7 type |
||
| Main Sequence Star (IV,V) <Hα 656.3nm> | ||||
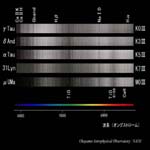
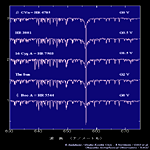
 O6-O9.5 type |
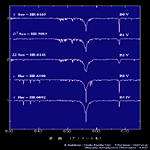 B0-B5 type |
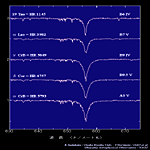 B6-A0 type |
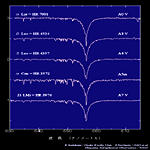 A0-A7 type |
|
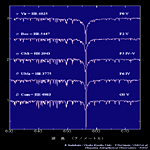 F0-G0 type |
 G0-G8 type |
|||
|
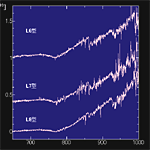
Main Sequence Star of low surface temperature (V) <wavelength 650-1000nm> | ||||
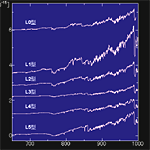 L0-5 type |
 L6-8 type |
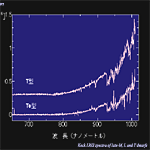 T type |
||
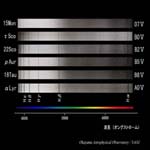
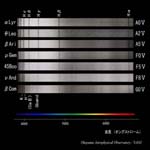
Luminosity Class
| <wavelength 380-700nm> | |||
|---|---|---|---|
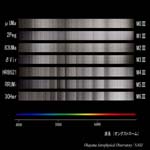
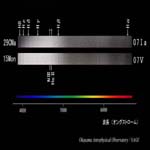 O7 type I, V |
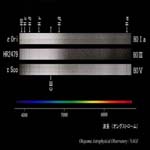 B0 type I, III, V |
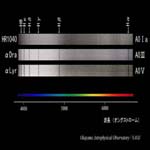 A0 type I, III, V |
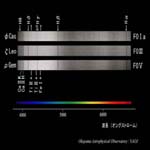 F0 type I, III, V |
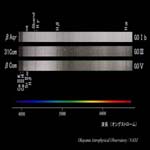 G0 type I, III, V |
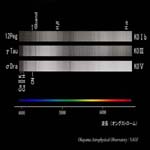 K0 type I, III, V |
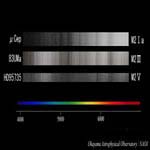 M2 type I, III, V |
|
| <Hα 656.3nm> | |||
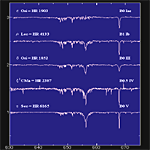 B0 type Ia,Ib,III,IV,V |
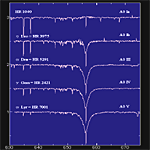 A0 type Ia,Ib,III,IV,V |
||
 Go to Submenu
Go to Submenu Go to Menu
Go to Menu
自然科学書出版 裳華房 SHOKABO Co., Ltd.